Why is it important to be able to translate into the Mandarin Chinese language?

Where is it spoken?
China – Taiwan – Singapore

Nº of speakers
1,118 million
Linguistic family
Sino-Tibetan – Sinitic
Bridging tradition and the future, Mandarin Chinese has established itself as one of the most influential languages in the world today. When it comes to global connectivity, the vibrant cities of Beijing, Shanghai and Taipei resonate with its tones and nuances.
With its vast geography, China is home to many dialects. But Modern Standard Mandarin is the key that holds this linguistic puzzle together.
together. It is not only a language that can help you travel, but it is the gateway to a literary world that combines ancient classics with cutting-edge contemporary literature. It is the language of business, technological innovation and unprecedented economic growth.
Translating or learning Mandarin Chinese language is more than just adding a language to your CV. It connects you to an expanding culture and economy that shows no signs of slowing down.
On the international stage, Mandarin has earned a place of honour as one of the official languages of the United Nations. If you’re looking to venture into international relations, business or technology, understanding Mandarin is definitely a star tool.

The most translated languages into Mandarin Chinese language
Learn to speak in Mandarin Chinese like a true native
Basic expressions in Mandarin Chinese
Advanced vocabulary
| 风水 (Fēngshuǐ) | Feng shui |
| 脑筋急转弯 (Nǎojīn jí zhuǎn wān) | Riddle |
| 美食家 (Měishí jiā) | Foodie |
| 跨文化 (Kuà wénhuà) | Intercultural |
| 情报 (Qíngbào) | Intelligence |
Other curiosities
- Tonal: Mandarin is a tonal language; therefore, the pitch used when pronouncing a word can alter its meaning.
- Written characters: Unlike traditional alphabets, written Chinese is character-based. To operate seamlessly, a Chinese newspaper demands around 2 or 3 thousand characters. Yet, in total, the language includes over 50,000.
- Antiquity: Mandarin is among the world’s oldest languages in written form, with records dating back over 3,000 years.
- Simplified vs Traditional: There are two writing systems for Mandarin: traditional, prevalent in Taiwan and Hong Kong, and simplified, adopted by the People’s Republic of China.
- Pinyin: This is a Romanisation scheme for Mandarin, using the Latin alphabet to phonetically transcribe the language.
- Simple Grammar: Unlike many other languages, Mandarin lacks verb conjugations and gender and number declensions.
- Cultural Influence: Numerous Chinese words reflect the country’s philosophy and culture.
For instance, the Chinese term for “crisis” is “危机” (wēijī) and consists of the characters for “danger” and “opportunity.” - Natural Origins: Numerous Chinese characters have their roots in pictorial depictions.
For instance, the character “木” (mù), meaning “tree,” strongly resembles the structure of a tree. - Chinese has no clear words for “yes” or “no”: Negative or Positive: The Chinese language does not possess distinct words for “yes” or “no.” Rather, responses are typically affirmative or negative verbs, depending on the query.
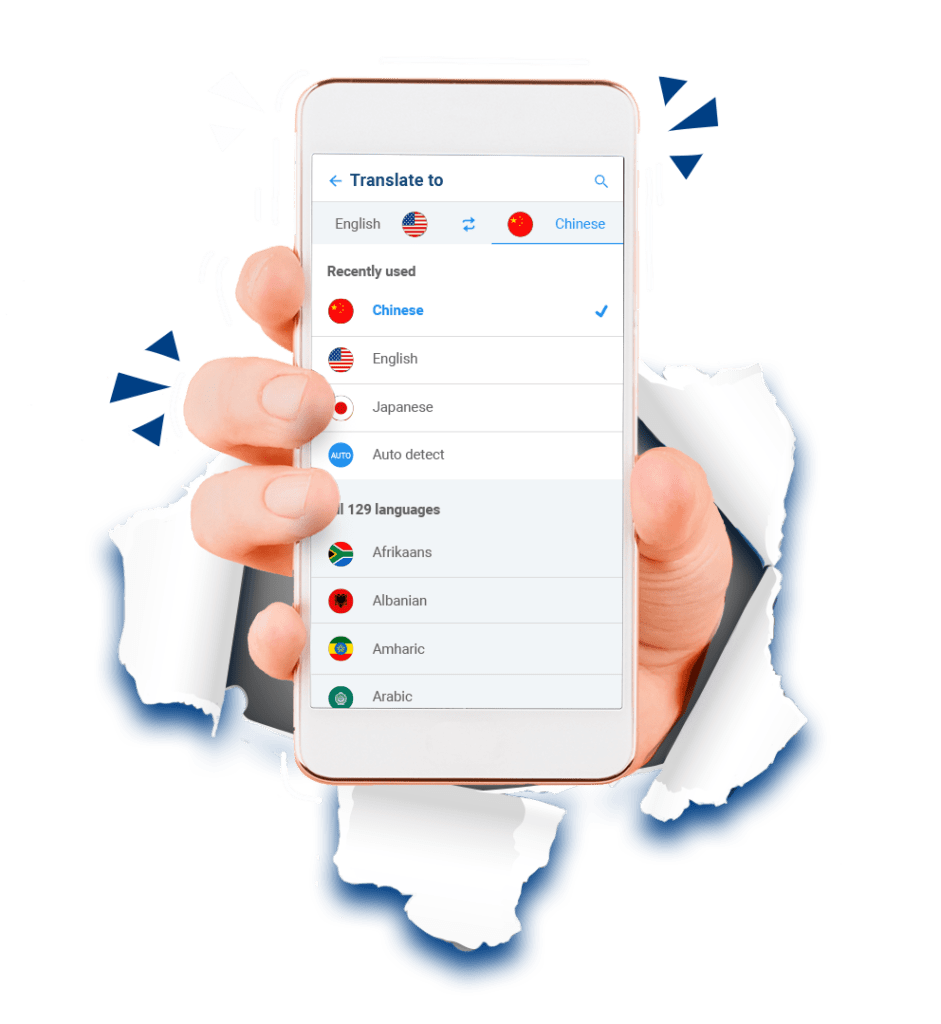
We offer Mandarin Chinese language support in multiple services
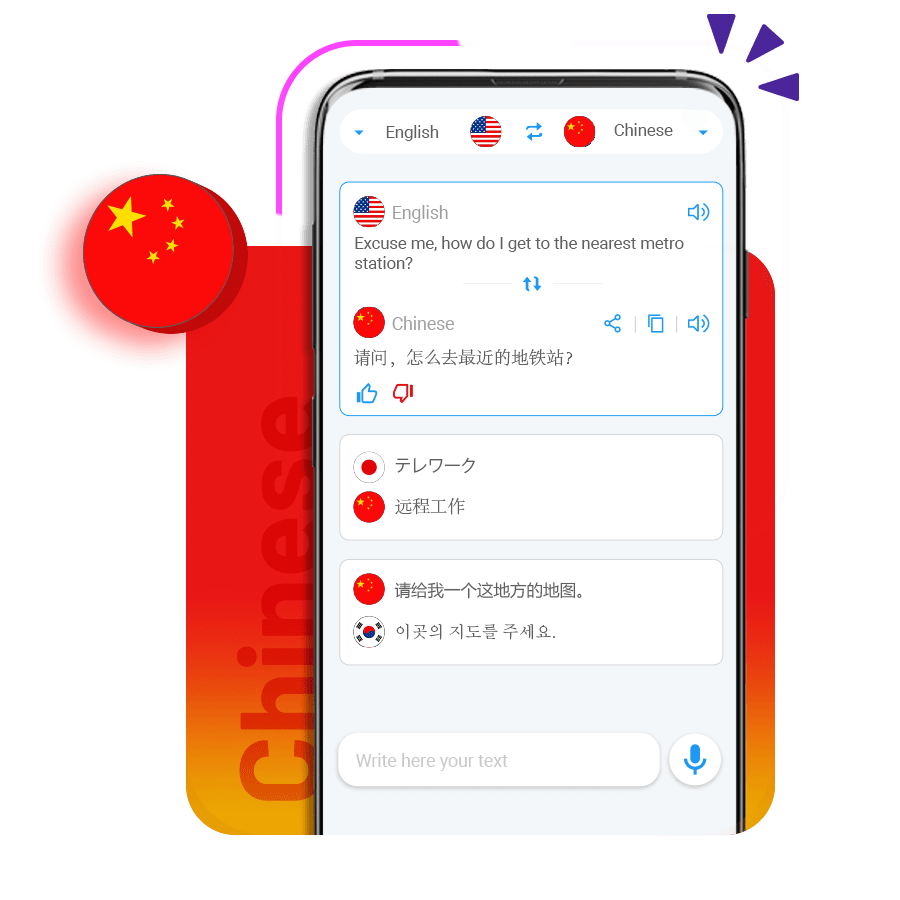
Audio and Text Translation
Mandarin Chinese language translator among over 125 available languages.

Remote Conversation Translation
Speak and translate to Mandarin Chinese with people anywhere in the world remotely.
Real-time Translation
Speak freely. Translate Mandarin Chinese instantly in real-time.

Learning with Smart Books
Expressions, essentials, culture, verbs, travel, and technical language all in one place.

Audio Playback of the Translation
Listen to the audio of the Mandarin Chinese translation to improve your pronunciation.

Voice Recognition
Speak freely and your app will translate for and to you.