If someone had mentioned augmented reality translation to our parents, they would’ve likely been considered delusional. Well, maybe not that extreme, but they definitely wouldn’t have believed it. Even today, there are many people who think this technology belongs in the realm of science fiction. However, as we’ll explore, augmented reality translation is not just real—it’s an innovation that’s here to stay.
Today, we’ll take you on a fascinating journey into the technological depths of augmented reality. We’ll explore how it’s applied to automatic translation and how it merges with artificial intelligence to enhance our daily lives. Plus, we’ll discuss the situations where augmented reality translation can be used and highlight its numerous benefits.
Buckle up, because this ride is about to get exciting!
What is “augmented reality translation”? Is it real?
Before we dive in, let’s clear one thing up: yes, it’s real—and how! This technology is not only real but is already being used in ways more common than you might imagine. From the bakery that made the bread you had for breakfast to the factory that assembled your car, augmented reality (AR) has found applications in fields as diverse as medicine and retail. But what exactly is it?
In simple terms, augmented reality involves overlaying images, texts, links, or information on a screen. It works through smart devices like smartphones, tablets, or specialized glasses. Essentially, AR can interpret a real-world image and combine it with specific data. But how does it work?
Explaining it in exact technical terms would be too complex, so let’s break it down in a simple way. Augmented reality translation, as the name implies, is based on AR itself. While that may sound obvious, this is precisely where the magic lies. Let’s take a closer look step by step.
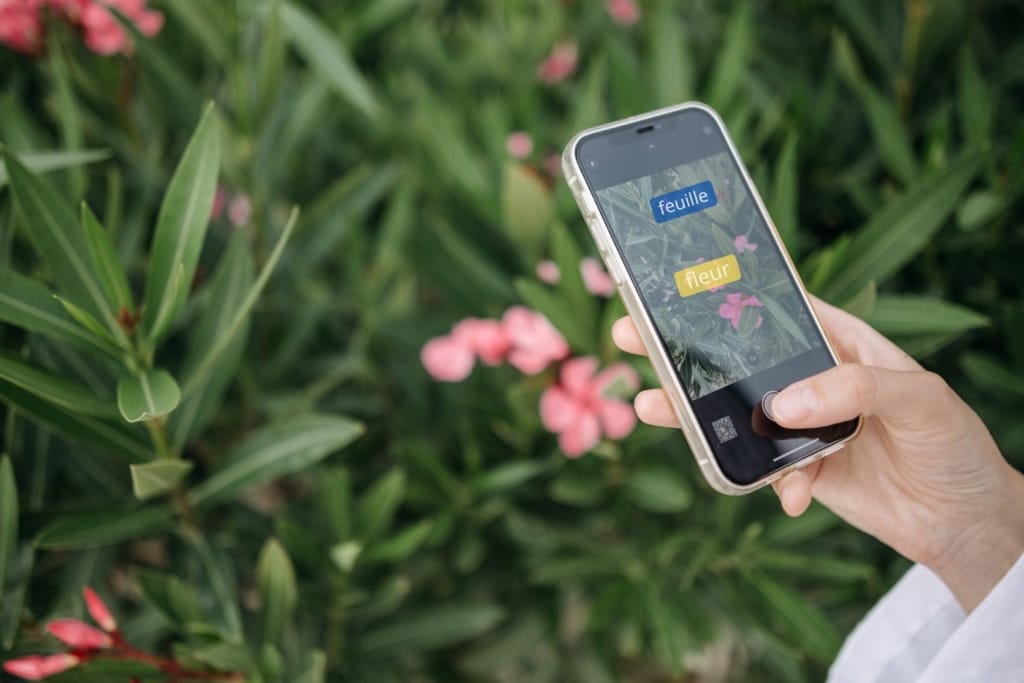

Step 1: Standardizing images
To explain how augmented reality translation works, we’ll break it down into stages. Why? Because something this complex is much easier to understand in smaller parts. Plus, seeing the full process makes it more engaging and informative. So, let’s get into it.
First, augmented reality requires creating a database of graphic elements from the “real world.” Developers feed this database with thousands upon thousands of images of objects, places, animals, or people. Thanks to artificial intelligence, AR software can learn that, for instance, a chair can come in thousands of shapes, colors, and sizes.
This information allows the system to compare a captured image from reality with its stored “realities.” In this way, the software learns to recognize a chair and interpret its variations without changing what it fundamentally is: a chair. This is why AR won’t confuse a chair with a table or a stool, even though they may share similar features. Which brings us to Step 2.
Step 2: Adding information
Once the images are captured and stored, it’s time to load the information. However, the type of information added depends heavily on the intended use of the AR technology. For example, AR used in a large hardware store will differ significantly from AR used in an car assembly plant—or in augmented reality translation software.
In short, the final purpose and user of the AR technology dictate the type of information loaded. AR is a tailor-made technology, designed to meet specific needs. For instance, in a retail setting, developers can link an image to details like price, availability, discounts, and variations. In a factory, components might be linked to part numbers, functions, and more.
The data-base of translation
When it comes to AR translation apps, developers upload information about the spelling and pronunciation of objects in one or even hundreds of languages. That’s right—AR and artificial intelligence are virtually limitless when it comes to the amount of information they can handle.
The most amazing thing about this process is that the database used to translate objects in AR is endless. The developers can add all the grammatical forms, pronunciations and colloquial forms of an element. So, you can access thousands of nouns, verbs and expressions in seconds.
Therefore, an image of a chair could be linked to a vast text detailing its history, how it’s made, or even the tree that provided the wood for its legs. But most importantly, it can tell you how to say “chair” in hundreds of languages. Surprised? Wait until you hear about the most fascinating stage in the process.
Step 3: Machine learning
Let’s stick with the chair example to keep things simple. Imagine pointing your phone’s AR translation app at a chair. Instantly, your phone tells you how to say “chair” in French, Italian, English, or Yoruba. And if you’re using a tool like Talkao’s AR translation app, you’ll have up to 125 languages to choose from.
Impressive, right? But here’s where it gets even better. Let’s say you’re looking at a designer chair that doesn’t resemble a conventional chair. Instead, it’s one of those avant-garde pieces that could pass for anything but a chair. It’s possible the app won’t recognize it or might even confuse it with a table or a cat.
Here’s the magic: you can tell the app that, despite its unconventional appearance, this is indeed a chair. And what happens next is astonishing.
The magic of AR’s self-learning
When the app makes a mistake, it “learns” from the error. It adds this new image of a chair to its database. This means the next person who uses the app, anywhere in the world, will already have this unique chair design stored and recognized. In short, the app learns from its mistakes and becomes smarter over time!
Now, you might be wondering: How does this help me? What can I do with such advanced technology? Sit tight, because the applications of augmented reality translation are the most exciting part of all.
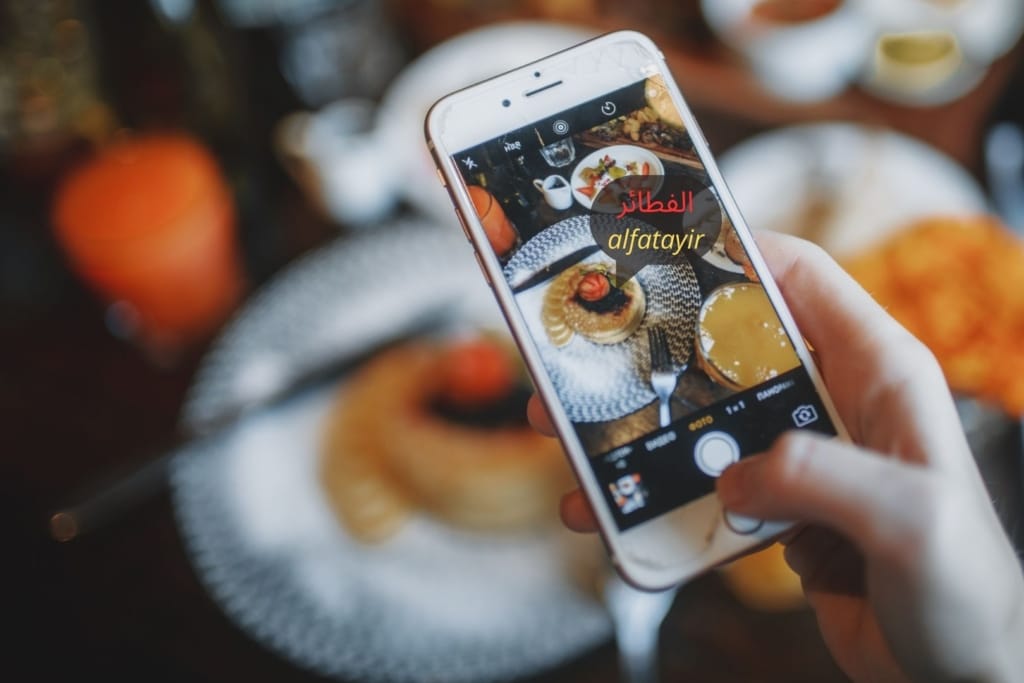

The uses of augmented reality translation
Once we’ve explored the behind-the-scenes process of translation with augmented reality, it’s time to put it into practice. As you may have already guessed, this technology has endless uses. It can be applied to something as simple as navigating during a trip or as complex as assisting in brain surgery. Without a doubt, augmented reality translation technology is one of the most significant breakthroughs in communication. Let’s take a closer look at some of its most common uses:
Translate while traveling
Imagine visiting a country where the language is completely unfamiliar to you. On top of that, they use a different alphabet, and many of the words you see or hear are entirely new to you. This is your first encounter with the language, and you have no idea how to even ask for directions. Terrifying, right? If you’ve ever been in this situation, you know exactly what we’re talking about.
Fortunately, this fear of being unable to communicate can be solved with your smartphone, without needing any technical expertise. By simply using the Talkao Augmented Reality Translation app, you can understand the meaning of everything around you. Additionally, you can translate audio and conversations in real time into over 125 languages. These translations can be voice-to-voice or voice-to-text. It’s like having subtitles for life… A true fantasy turned into reality!
Business applications
Recently, we discussed how languages could play a key role in your career. This small example highlights the critical role language plays in business. A minor misunderstanding or a translation error can have disastrous consequences. In fact, depending on the context, a single mistranslated word could jeopardize a promising business deal.
With augmented reality translation, these errors are minimized and become almost imperceptible. This technology not only translates conversations into text but also goes beyond. The Talkao Augmented Reality Translation app allows for smooth and seamless communication.
Moreover, it can integrate with a camera translator to convert texts into your language, regardless of the original alphabet. Imagine being able to read and immediately sign a contract without involving a specialized translator. Besides saving money, this technology significantly reduces decision-making time.
Language learning
This is perhaps one of the most fun and useful applications of augmented reality translation. While practicing a language, you can learn the names of thousands of objects and places using just your smartphone. By pointing your Android or iOS device’s camera at anything, the augmented reality app will identify it.
In seconds, the app provides an image with small labels indicating the name of each element on the screen. Its extensive image library includes thousands of objects, locations, animals, landscapes, and shapes. Additionally, the app displays the name of the item in your chosen language, along with its pronunciation, regardless of the alphabet it uses.
As you can see, the augmented reality translation app is not a concept from a sci-fi movie… It’s already here and available for you! You can use it in any field, and slowly but surely, language barriers will start to fade away.